Acidity-Targeted Drug Delivery Systems
Tumor acidity-targeted strategies for safer, more effective cancer therapy and drug resistance reversal
Cancer therapies often suffer from systemic toxicity or unsatisfactory efficacy, limiting their therapeutic window. To address these challenges, I developed tumor acidity-targeted drug delivery strategies that modify the tissue tropism of therapeutics, thereby expanding the therapeutic window.
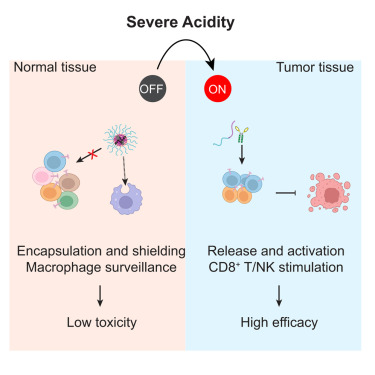
For instance, stimulatory cytokines like interleukin-2 (IL-2) can augment lymphocyte-mediated anti-tumor responses but are hindered by systemic toxicity. I engineered a strategy to mask IL-2 toxicity in normal tissues, allowing it to be effective only in tumor. This resulted in a new IL-2 therapy with over 100-fold reduced toxicity. This work was recognized with a Young Investigator Award and is currently under further development.
Additionally, I tackled chemotherapy resistance by creating a pH-switchable drug delivery system that improves the retention of chemotherapeutic agents within cancer cells. This system significantly enhances anti-tumor efficacy by ensuring drugs remain inside cancer cells longer, maximizing their therapeutic impact. This approach offers a highly tumor-specific strategy compared to traditional drug design, and therapies based on this technology are under development by biotech companies.
Selected Publications
-
Feng, Q.; Huang, G.; Pantoja, R.; Sun, Z.; Li, W.; Torres, K.; Wilhelm, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, T.; Han, R.; Gao, J. Ultra-pH Sensitive Nanoparticles Increase Therapeutic Index of IL-2-Fc. J. Immunother. Cancer 10, A1380 (2022).
This abstract presents a novel severe acidity-targeted strategy to control cytokine therapy toxicity, achieving over 100-fold decrease in systemic IFN-γ levels in vivo.
-
Feng, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Chen, Q.; Sun, J.; Shi, X.; Ding, B.; Yu, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X. One-Step Microfluidic Synthesis of Nanocomplex with Tunable Rigidity and Acid-Switchable Surface Charge for Overcoming Drug Resistance. Small 2017, 13, 1603109. PMID: 27943612.
This paper describes an acidity-targeting strategy to improve chemotherapy effectiveness, achieving over 10-fold increase in tumor growth inhibition in vivo.
-
Huang, T.; Feng, Q. (Co-first author); Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Sun, Z.; Wilhelm, J.; Huang, G.; Vo, T.; Sumer, B. D.; Gao, J. Tumor-Targeted Inhibition of Monocarboxylate Transporter 1 Improves T-Cell Immunotherapy of Solid Tumors. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2021, 10, e2000549. PMID: 32431046.
This work describes the tumor specific delivery of an inhibitor of lactic acid transporter to reverse tumor acidosis and related immunosuppression, improving antitumor efficacy at 50-fold reduced doses.