Microfluidic Synthesis Method
Microfluidic technology for precise control of nanoparticle structure and function in drug delivery
Nanoparticles are promising therapeutic platforms for drug delivery. However, controlling their physical properties—such as size, surface charge, rigidity, and internal structure—is crucial for optimizing their interaction with biological systems and improving therapeutic outcomes.
While microfluidic synthesis is widely used for producing nanoparticles with uniform size and continuous production (a key factor in the clinical translation of lipid nanoparticle-based mRNA vaccines), limited attention has been given to the precise control of nanoparticle structure during synthesis. During my graduate studies, I developed microfluidic technology that allows for the precise control of nanoparticle structures directly on-chip.
I established methods to generate nanoparticles with tunable size, surface charge, rigidity, and core-shell configurations. These structural variations significantly influenced nano-bio interactions and drug delivery efficacy. My research demonstrated that small, rigid nanoparticles exhibit higher cellular uptake and improved tumor targeting efficiency compared to larger or more flexible ones.
This work has important implications for the design of effective drug delivery systems and contributes to advancing the field of nanomedicine.
Selected Publications
-
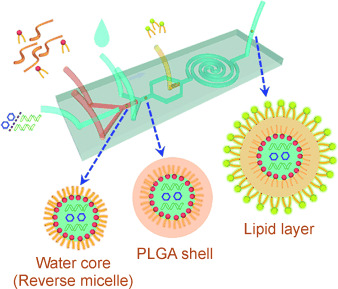
Zhang, L.; Feng, Q. (Co-first author); Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Shi, X.; Jiang, X. Microfluidic synthesis of rigid nanovesicles for hydrophilic reagents delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3952. PMID: 25704675.
This paper introduces a microfluidic method to control nanoparticle core structures, leading to the development of rigid nanosized capsules for encapsulating various hydrophilic reagents, including proteins, small molecules, and nucleic acids.
-
Feng, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Hu, G.; Sun, J.; Jiang, X. Microfluidic based high throughput synthesis of lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles with tunable diameters. Biomicrofluidics 2015, 9 (5), 052604. PMID: 26180574.
This study presents a microfluidic method for tuning the size of core-shell type nanoparticles.
-
Feng, Q.; Sun, J.; Jiang, X. Microfluidics-mediated assembly of functional nanoparticles for cancer-related pharmaceutical applications. Nanoscale 2016, 8 (25), 12430-12443. PMID: 26864887.
This publication summarizes basic physicochemical principles and biological applications of microfluidic platforms in nanoparticle formulation.